LESSON 2
The Gulf Stream and Global Currents: Why They Matter

Introduction:
The Ocean’s Superhighways
Imagine invisible rivers flowing across the oceans—huge, powerful streams moving warm and cold water all around the world. These are ocean currents, and they’re critical for life on Earth.The Gulf Stream, one of the most famous, acts like a giant conveyor belt, moving heat from the tropics to the poles. Without ocean currents, many regions would be too hot, too cold, or too dry to support life as we know it.
1. What Is the Gulf Stream?
The Gulf Stream is a warm ocean current that begins in the Gulf of Mexico, flows up the east coast of the United States, and then heads across the Atlantic toward Europe. It’s part of a larger system called the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC).
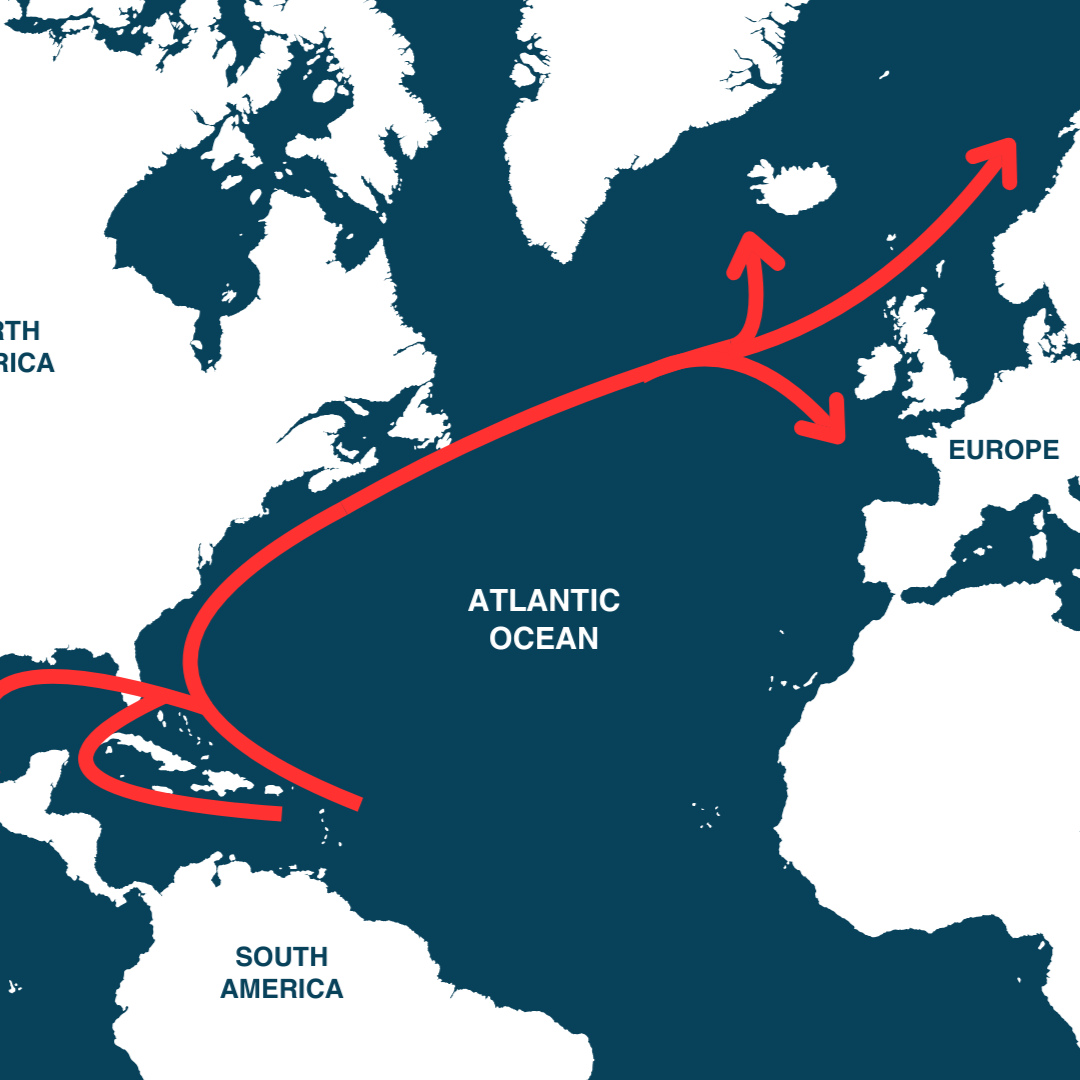
Why is it important?
- It carries warm water north, making climates in places like Britain and Western Europe much milder than they otherwise would be.
- It helps regulate weather patterns, from hurricanes in the Atlantic to rain in Europe and Africa.
Did you know?
If the Gulf Stream slowed or stopped, Europe could become much colder, and weather patterns around the world could drastically shift.
2. Other Major Global Currents
The Gulf Stream is just one part of a much larger system called the Global Conveyor Belt (or Thermohaline Circulation). This system moves water around the globe based on differences in temperature (thermo) and salinity (haline).
Key Currents Around the World
Fun Fact
Water from the surface ocean can take over 1,000 years to travel all the way around the Global Conveyor Belt!
3. How Currents Shape Climate and Ecosystems
Ocean currents don’t just move water—they move life.
Fun Fact
Areas where warm and cold currents meet (like the Grand Banks off Canada) are some of the most productive marine ecosystems on Earth!
Conclusion
Currents – The Ocean’s Lifeblood
Ocean currents are like Earth's circulatory system, moving vital heat, nutrients, and life across the globe. The Gulf Stream, and the Global Conveyor Belt it’s part of, help stabilize climate, fuel biodiversity, and connect distant parts of our world in amazing ways.
By understanding currents, we get a clearer picture of how connected our planet truly is.
Key Takeaways:
The Gulf Stream moves warm water from the Gulf of Mexico to Europe, shaping climate and weather.
Global ocean currents form a vast "conveyor belt" that regulates temperature, oxygen, and nutrient flow.
Currents impact ecosystems, weather, and even human activities like fishing and farming.
Changes in currents could have major consequences for Earth's climate and food supply.
NEXT LESSON
What Are El Niño and La Niña?
Next, we’ll explore El Niño and La Niña—powerful natural phenomena that arise when ocean currents and temperatures change in the Pacific Ocean, with global consequences for weather, farming, and even coral reefs.

















